Weightlifters & All-Cause Mortality
Weightlifters & All-Cause Mortality
A 2016 study in Preventative Medicine concluded that adults who strength-trained at least twice a week had a 46% reduction in mortality compared to those who did not strength train.
This multi-year study followed the health of 30,000 adult participants, including the respondents through death certificate data from the National Center for Health Statistics National Death Index. Unlike aerobic exercise’s well-established effects, strength training has only recently garnered attention for its benefits in regaining muscle mass and strength often depleted with age and disability. While any regular physical activity has consistent and powerful relationships with longer life expectancy, the study aimed to prove that strength training also plays an important role in decreasing premature mortality.
Kraschnewski JL et al., Prev Med (2016)

Weightlifters & All-Cause Mortality
A 2016 study in Preventative Medicine concluded that adults who strength-trained at least twice a week had a 46% reduction in mortality compared to those who did not strength train.
This multi-year study followed the health of 30,000 adult participants, including the respondents through death certificate data from the National Center for Health Statistics National Death Index. Unlike aerobic exercise’s well-established effects, strength training has only recently garnered attention for its benefits in regaining muscle mass and strength often depleted with age and disability. While any regular physical activity has consistent and powerful relationships with longer life expectancy, the study aimed to prove that strength training also plays an important role in decreasing premature mortality.
Kraschnewski JL et al., Prev Med (2016)
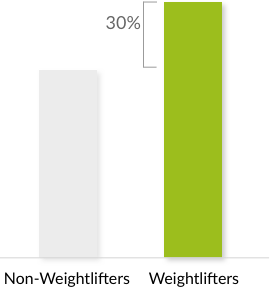
 Weightlifters & Sleep Quality
Weightlifters & Sleep Quality
According to a seminal 1997 study from Harvard Medical School, adults who participated in 10 weeks of strength training 3 days a week found a 30% improvement in their sleep quality.
The study was a randomized, controlled, 1O-week clinical trial in which subjects with varying levels of diagnosed depression were placed in either a strength-training program or a health-education program. Sleep quality was measured before and after training with a well-validated questionnaire. Participants in the strength training group followed a high-intensity regimen training the large muscle groups, 3 days a week for 10 weeks. Strength gains were expected. But their confirmation that strength training is directly linked to sleep quality was groundbreaking, calling for further research to confirm and extend these findings.
Singh, et al. Sleep (1997)
Weightlifters & Sleep Quality
 Weightlifters & Cholesterol
Weightlifters & Cholesterol
According to the 2009 American College of Sports Medicine position stand on Exercise and Physical Activity, studies have proven that strength training has powerful benefits on cholesterol levels, such as:
it increases HDL cholesterol by as much as 21%
it decreases low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol by as much as 23%
it reduces triglycerides by as much as 18%
The ACSM position stand on Exercise and Physical Activity is published once a year with what the ACSM board has deemed the issues and discoveries most critical to exercise and physical activity. Section 1 briefly reviews the structural and functional changes that characterize normal human aging, Section 2 considers the extent to which exercise and physical activity can influence the aging process, and Section 3 summarizes the benefits of both long-term exercise and physical activity and shorter-duration exercise programs on health and functional capacity.
American college of sports medicine et al.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009 Jul;41(7):1510-30. (doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181a0c95c)

Weightlifters & Cholesterol
According to the 2009 American College of Sports Medicine position stand on Exercise and Physical Activity, studies have proven that strength training has powerful benefits on cholesterol levels, such as:
it increases HDL cholesterol by as much as 21%
it decreases low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol by as much as 23%
it reduces triglycerides by as much as 18%
The ACSM position stand on Exercise and Physical Activity is published once a year with what the ACSM board has deemed the issues and discoveries most critical to exercise and physical activity. Section 1 briefly reviews the structural and functional changes that characterize normal human aging, Section 2 considers the extent to which exercise and physical activity can influence the aging process, and Section 3 summarizes the benefits of both long-term exercise and physical activity and shorter-duration exercise programs on health and functional capacity.
American college of sports medicine et al.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009 Jul;41(7):1510-30. (doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181a0c95c)
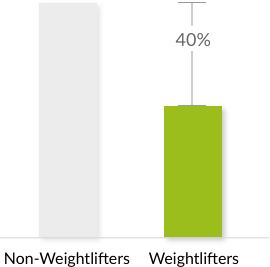
 Weightlifters & Decreased Fat
Weightlifters & Decreased Fat
A 1996 study published in the Journal of Applied Physiology focused on how far diet and high intensity strength training could impact the breakdown of bad fatty tissue in middle-aged men. The most significant impact was the resulting 40% decrease in visceral fat.
The selected group of middle-aged male participants in the study performed 8 to 12 reps of these strength exercises 3 days a week: leg extension, leg flexion, super pullover, chest press, chest cross, shoulder press, tricep extension, bicep curls, and setups. When retested after the trials were over, body weight was down approximately 10% and 40% of fatty tissue had been lost.
Ross et al. J Appl Physiol (1996)
Weightlifters & Decreased Fat


We are a licensed life insurance agent* in all 50 states.
View our licenses
We negotiated lower rates on life insurance using science and data.
View our research
By weightlifters for weightlifters. Our team is comprised of health conscious people who overcame their own health challenges with healthy habits, exercise, and nutrition.
Meet our team